How Much Does It Cost to Develop Mobile Apps for Logistics?
A few years ago, the logistics sector was synonymous with disorganised procedures, extensive paperwork, ongoing supervision, and manual labour. Today, however, the business has undergone a full transformation for all the right reasons thanks to technological advancements and the introduction of mobile apps for logistics.
Isn’t that incredible? With the use of mobile apps, tasks that once required standing in lengthy lines and waiting for hours merely to mail a package may now be completed with a simple tap.
Mobile apps for logistics management not only facilitate effective communication between shippers and drivers but also optimise routes, cut costs, make life easier, and promote business growth by raising individual productivity levels.

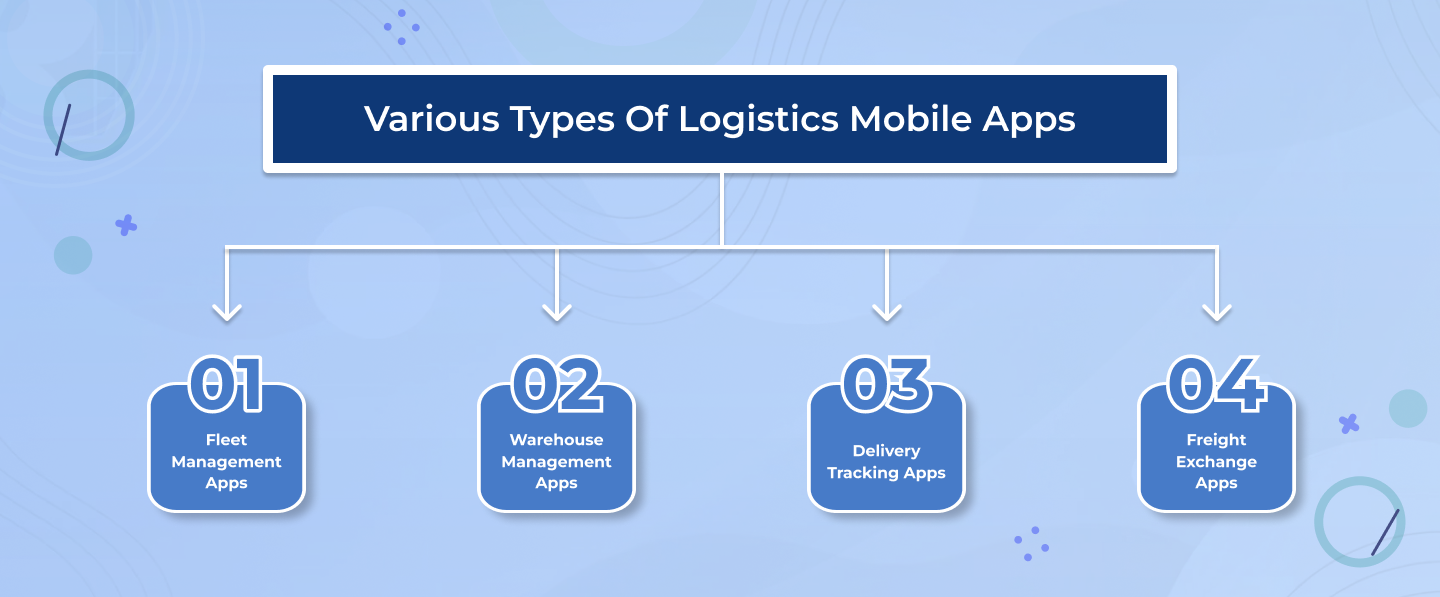
There are various types of logistics mobile apps that cater to different aspects of the logistics industry. Here are four common types:
1. Fleet Management Apps:
Fleet management apps help logistics companies efficiently manage and track their fleet of vehicles. These apps provide features such as real-time vehicle tracking, route optimization, fuel monitoring, driver management, and maintenance scheduling. They help streamline operations, improve productivity, and enhance overall fleet performance.
2. Warehouse Management Apps:
Warehouse management apps assist in optimizing and controlling warehouse operations. They provide functionalities like inventory management, order fulfillment, barcode scanning, stock tracking, and shipment tracking. These apps enable warehouse staff to monitor inventory levels, track products, and streamline the order fulfillment process, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced errors.
3. Delivery Tracking Apps:
Delivery tracking apps are designed to provide real-time visibility to customers and logistics companies about the status and location of deliveries. They often include features like package tracking, estimated delivery times, delivery notifications, and proof of delivery. These apps enhance customer experience by keeping them informed and allow logistics companies to monitor and manage their delivery operations effectively.
4. Freight Exchange Apps:
Freight exchange apps act as a platform connecting shippers and carriers. These apps facilitate the process of finding available trucks for transportation and matching them with suitable loads. They provide features like load posting, freight bidding, rate negotiation, and communication tools. Freight exchange apps streamline the process of freight booking, reduce empty miles, and help optimize the utilization of transportation resources.
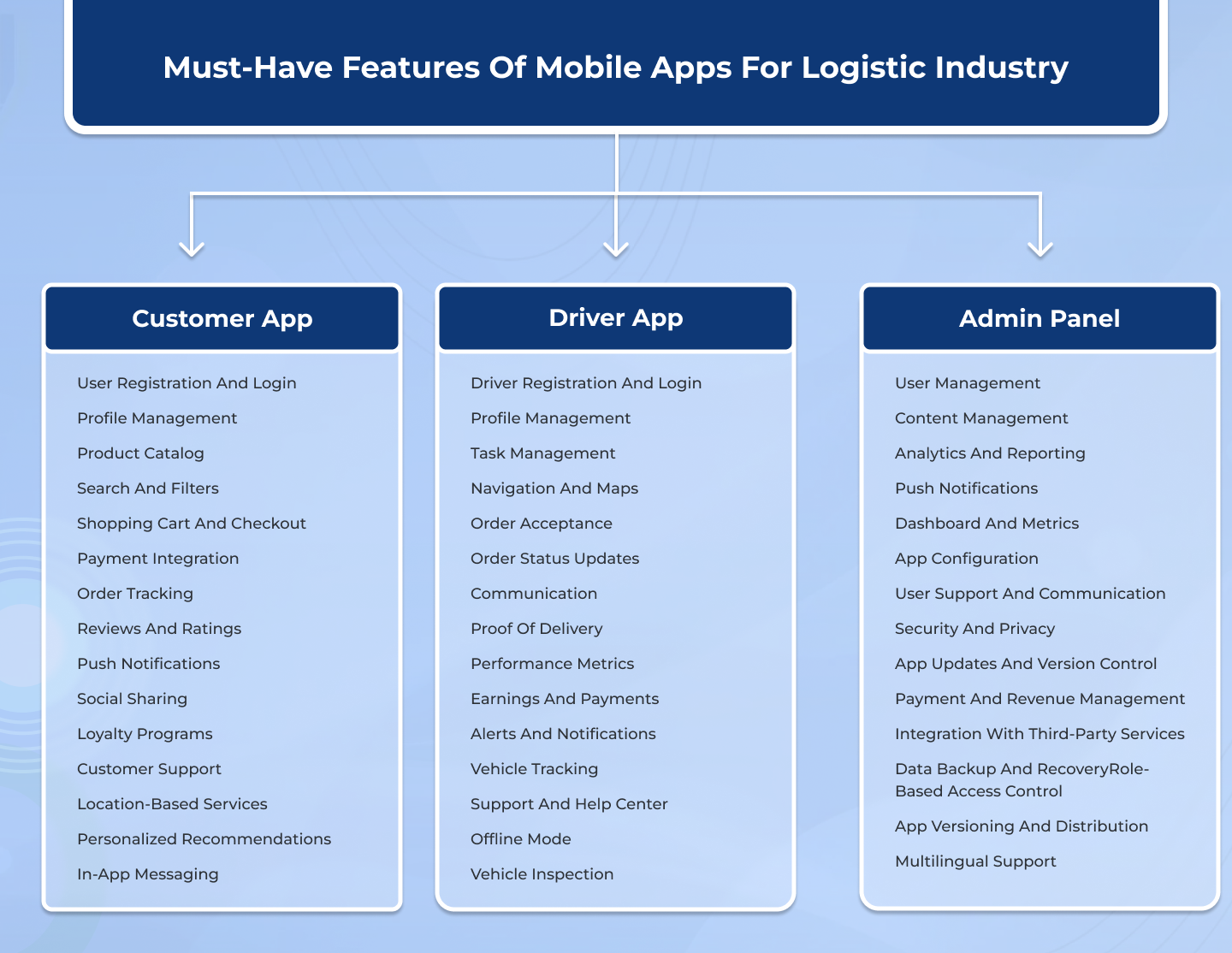
Must-Have Features of Mobile Apps For Logistic Industry
1. Customer App
1. User Registration and Login:
Customers can create an account and log in using their credentials or social media accounts to access personalized features and information.
2. Profile Management:
Users can manage their personal information, update preferences, and customize their profiles as per their requirements.
3. Product Catalog:
An interactive catalog displaying products or services offered by the business, with detailed descriptions, images, and pricing information.
4. Search and Filters:
A search bar and filters to help users find specific products or services based on their preferences, such as price range, category, location, etc.
5. Shopping Cart and Checkout:
Users can add items to their virtual shopping cart, review their selections, and proceed to the secure checkout process to complete the purchase.
6. Payment Integration:
Integration with various payment gateways to facilitate secure and seamless online transactions, supporting credit/debit cards, mobile wallets, or other payment methods.
7. Order Tracking:
Real-time updates and notifications regarding the status of orders, allowing users to track their deliveries or services.
8. Reviews and Ratings:
Users can leave feedback, ratings, and reviews for products or services, helping others make informed decisions and providing valuable feedback to the business.
9. Push Notifications:
Instant alerts and notifications to keep customers informed about new product arrivals, promotions, discounts, order updates, or personalized offers.
10. Social Sharing:
Integration with social media platforms to enable users to share products, offers, or their experiences with friends and followers.
11. Loyalty Programs:
A loyalty program or reward system that incentivizes customers for their repeat business, providing exclusive discounts, rewards, or points accumulation for future benefits.
12. Customer Support:
In-app customer support channels such as live chat, messaging, or a helpline to assist users with inquiries, issues, or complaints.
13. Location-based Services:
Utilizing GPS technology to provide location-based services, such as finding nearby stores, services, or displaying relevant offers based on the user’s current location.
14. Personalized Recommendations:
AI-powered algorithms that analyze user preferences and purchase history to provide personalized product recommendations or offers.
15. In-app Messaging:
A communication channel between customers and the business to facilitate inquiries, feedback, or direct interaction with customer service representatives.
16. These are just some of the common features found in customer apps.
The actual features may vary depending on the specific industry, business model, and target audience of the mobile app.
2.Driver App
1. Driver Registration and Login:
Drivers can create an account and log in using their credentials to access their personalized dashboard and functionalities.
2. Profile Management:
Drivers can manage their personal information, update their availability, upload documents, and customize their profiles.
3. Task Management:
A dashboard displaying assigned tasks, pickups, or deliveries, along with relevant details such as customer information, location, and deadlines.
4. Navigation and Maps:
Integration with GPS and mapping services to provide real-time navigation, route optimization, and directions to the pickup and drop-off locations.
5. Order Acceptance:
Drivers can accept or decline incoming orders or requests based on their availability or preferences.
6. Order Status Updates:
Drivers can update the status of each order, such as “picked up,” “en route,” or “delivered,” allowing customers and businesses to track progress.
7. Communication:
In-app messaging or chat functionality to facilitate communication between drivers and customers or dispatchers, enabling quick updates, clarifications, or issue resolution.
8. Proof of Delivery:
Drivers can capture and upload proof of delivery, such as signatures, photos, or electronic signatures, to confirm successful completion of a delivery.
9. Performance Metrics:
Drivers can access performance metrics, such as completed deliveries, average delivery time, ratings, or earnings, to track their performance and improve efficiency.
10. Earnings and Payments:
Drivers can view their earnings, track payments, and manage their payment preferences, such as bank account details or digital wallets.
11. Alerts and Notifications:
Real-time notifications and alerts regarding new orders, changes in pickup or delivery details, traffic updates, or any relevant information.
12. Vehicle Tracking:
Utilizing GPS technology to track the driver’s location and provide real-time updates to customers or dispatchers.
13. Support and Help Center:
In-app access to support resources, FAQs, or a helpline to assist drivers with inquiries, issues, or emergencies.
14. Offline Mode:
The ability to work in offline mode, allowing drivers to access critical information and perform tasks even in areas with limited or no internet connectivity.
15. Vehicle Inspection:
Drivers can perform vehicle inspections and report any damages or issues, ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations.
3.Admin Panel
1. User Management:
The ability to manage user accounts, including creating new accounts, updating user information, and managing user roles and permissions.
2. Content Management:
A feature that allows administrators to manage the app’s content, such as adding, editing, or removing text, images, videos, or other multimedia elements.
3. Analytics and Reporting:
Tools to gather and analyze data on app usage, user behavior, and performance metrics, providing insights into user engagement, popular features, and areas for improvement.
4. Push Notifications:
The ability to send targeted push notifications to app users, allowing administrators to communicate important information, updates, or promotions.
5. Dashboard and Metrics:
An overview dashboard that displays key performance indicators, metrics, and real-time statistics about the app’s usage, downloads, and other relevant data.
6. App Configuration:
The ability to configure app settings and preferences, such as branding elements, app appearance, notification settings, and other customizable options.
7. User Support and Communication:
Features to provide support and communicate with app users, such as responding to user inquiries, providing help documentation, or managing user feedback.
8. Security and Privacy:
Tools to manage app security features, including user authentication, data encryption, and permissions management to ensure the privacy and integrity of user data.
9. App Updates and Version Control:
The ability to manage app updates, including releasing new versions, bug fixes, and feature enhancements, and controlling the deployment process.
10. Payment and Revenue Management:
Features to manage in-app purchases, subscriptions, advertising, or other revenue-generating aspects of the app, including transaction tracking and financial reporting.
11. Integration with Third-Party Services:
The ability to integrate with external services or APIs, such as payment gateways, analytics platforms, customer relationship management systems, or social media platforms.
12. Data Backup and Recovery:
Tools to perform regular data backups and ensure the ability to restore data in case of any unforeseen circumstances or system failures.
13. Role-Based Access Control:
The ability to define different user roles and permissions within the admin panel, allowing specific access and functionalities based on the user’s role or responsibility.
14. App Versioning and Distribution:
Tools to manage different app versions, control the distribution of beta versions or test builds, and monitor app store submissions and approvals.
15. Multilingual Support:
The ability to manage app content and localization for multiple languages, allowing administrators to add, edit, or translate app content to cater to different regions or user preferences.
How Much Does the Development of Mobile Apps For Logistics Costs?
The cost to develop a mobile logistics application relies on a number of variables. There are many different kinds of apps with diverse business models in this enormous sector. And each of them has unique characteristics and objectives.
The number of features you add, the technology stack you select, the platforms you intend to target, the size of your app, and the location of the logistics app development firm you engage will all have an impact on the development cost.
In order to determine the precise amount you will have to invest in creating mobile apps for the logistics business, it is crucial for you to first explain your requirements. To offer you an approximate estimate, it will cost you between $30 and $40k to develop an app with all of the aforementioned features and using the specified tech stack.
However, if you want to integrate some advanced features in your logistics app, the charges can go higher. If you are on a low budget – you can consider building a cross-platform mobile application to market your business ASAP.